Sparse Signal Models
Contents
12. Sparse Signal Models¶
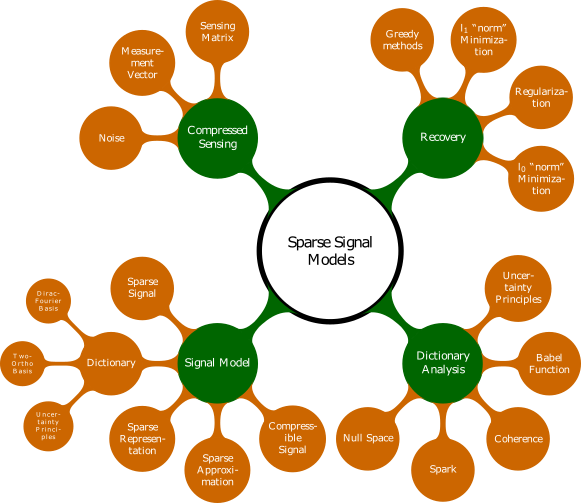
12.1. Outline¶
In this chapter we develop initial concepts of sparse signal models.
We begin our study with a review of solutions of under-determined systems. We build a case for solutions which promote sparsity.
We show that although the real life signals may not be sparse yet they are compressible and can be approximated with sparse signals.
We then review orthonormal bases and explain the inadequacy of those bases in exploiting the sparsity in many signals of interest. We develop an example of Dirac Fourier basis as a two ortho basis and demonstrate how it can better exploit signal sparsity compared to Dirac basis and Fourier basis individually.
We follow this with a general discussion of redundant signal dictionaries. We show how they can be used to create sparse and redundant signal representations.
We study various properties of signal dictionaries which are useful in characterizing the capabilities of a signal dictionary in exploiting signal sparsity.
In this chapter, our signals of interest will typically lie in
the finite
We will be concerned with different representations of our signals of interest in
12.2. Sparsity¶
We quickly define the notion of sparsity in a signal.
We recall the definition
of
where
More generally if
where
Sometimes we simply say that
An even more general definition of sparsity is the degrees of freedom a signal may have.
Example 12.1 (Degrees of freedom on the surface of a sphere)
Consider all points on the surface of a unit sphere in
For every point
Thus if we choose the values of
Thus the number of degrees of freedom
Such a surface represents a manifold in the ambient Euclidean space.
Of special interest are low dimensional manifolds where the number of degrees of freedom